Summary: An anechoic chamber is primarily used for measuring electromagnetic interference (EMI) and electromagnetic susceptibility (EMS). The size of the anechoic chamber and the selection of RF absorbing materials are primarily determined by the size of the device under test (DUT) and the testing requirements.
A fully anechoic chamber reduces the interference of external electromagnetic signals on the test signal. At the same time, the RF absorbing materials can minimize the impact of multipath effects on test results caused by reflections from walls and ceilings. It is suitable for emission, susceptibility, and immunity tests. The conditions in free space can be simulated in a fully anechoic chamber. Compared to two other test sites, the floor, ceiling, and walls of the anechoic chamber have less reflection, are less affected by the external environment, and are not influenced by external weather conditions.
Main Purpose: An anechoic chamber is used to simulate open-field conditions and is also used for measuring electromagnetic interference (EMI) and electromagnetic susceptibility (EMS). The size of the anechoic chamber and the selection of RF absorbing materials are primarily determined by the size of the device under test (DUT) and the testing requirements. It is divided into the 1m method, 3m method, or 10m method. Our company can customize various types of anechoic chambers for customers to meet their precise testing needs.
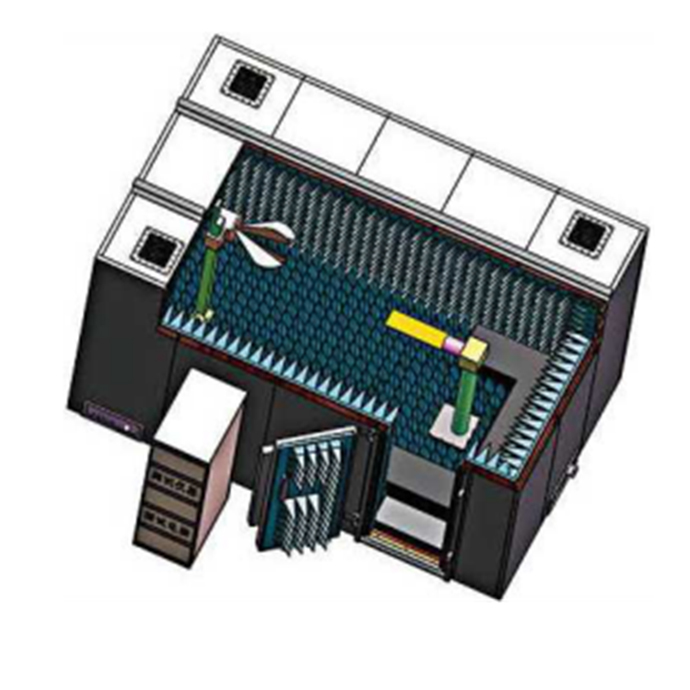
Microwave Darkroom Structure:
3D diagram of the microwave darkroom
Bolt or weld assembly
Performance Index:
Magnetic field: 14KHz, 70dB, 200KHzm100dB
Plane waves: 1 MHz-300MHz m 100dB 300MHz~1GHz with 100dB
Microwave: 1GHz-10GHz n 80dB
Testing Method: National Standard GB12190-90